Abstract
Developing world models that understand complex physical interactions is essential for advancing robotic planning and simulation. However, existing methods often struggle under data scarcity and contact-rich dynamics. We propose ContactGaussian-WM, a differentiable physics-grounded rigid-body world model that learns physical laws directly from sparse videos. Our framework uses a unified Gaussian representation for visual appearance and collision geometry, and an end-to-end differentiable learning pipeline that differentiates through a closed-form physics engine to infer physical properties. Extensive simulations and real-world evaluations show strong performance in complex scenarios and robust generalization.
Method Overview
ContactGaussian-WM uses a unified Gaussian representation for both appearance and collision geometry. A differentiable Gaussian collision detector computes contact points, which are fed into a complementarity-free contact dynamics model to update physical states. A 3DGS renderer then predicts the next frame, enabling end-to-end learning from sparse videos.
We adopt a two-stage optimization strategy: (1) scene initialization with isotropic spherical Gaussians, and (2) joint refinement of geometry and physical parameters using differentiable dynamics and rendering. This design supports stable training and accurate modeling of contact-rich interactions.
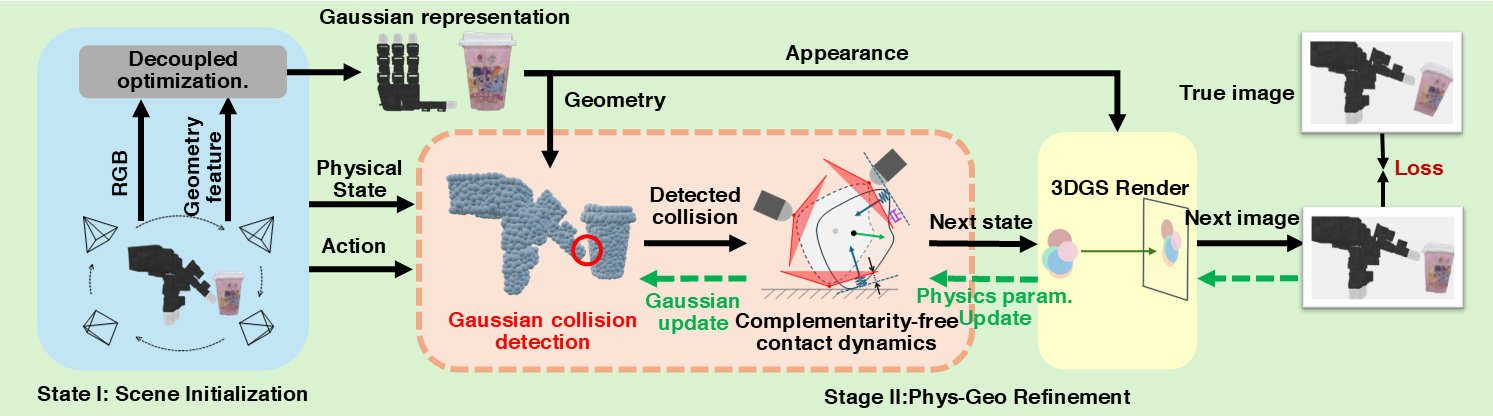
We first initialize a scene with a unified spherical Gaussian representation, then jointly refine physics and geometry: given the current physical state and action, the differentiable collision detector uses Gaussian geometry to compute contact points, which are fed into the complementarity-free contact dynamics model to compute the next physical state, and the 3DGS renderer generates the next image. The pipeline is fully differentiable for end-to-end learning.
BibTeX